A terminology problem odds ratio versus odds Author William Gould, StataCorp James Hardin, StataCorp Unfortunately, the language used to describe statistical terms is not used uniformly across fields One example of this is odds and odds ratio Economists especially refer to what others call the odds as the odds ratio Below, we will be careful to define our terms Proof thatWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative riskFor instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an odds ratio

A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
Odds ratio versus relative risk interpretation
Odds ratio versus relative risk interpretation- · L'Odds Ratio (OR) est le rapport des cotes d'exposition Cette notion de cote est semblable à celle utilisée pour les paris sportifs Dans notre exemple la cote chez les personnes exposées est de 30 contre 70 Chez les non exposés, cette cote est de 10 pour 90 Ainsi l'OR est égal à (30/70)/(10/90) = 39 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program At the start of the school year they impose the new



Nccmt Ure Relative Risk It S Easy To Calculate And Interpret Youtube
Common pitfalls in statistical analysis Odds versus risk In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables · Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases of medium to highAs an example, an odds ratio of 11 would suggest a 10% increase in
· After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the study · Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Published on December 14, 15 by Howard Herrell, MD Many great things have been written about the difference between Odds Ratios (OR) and Relative Risks (RR) Every medical student at some point has been taught the difference Yet these statistical terms are confused and misused every day in both the writing of and the · Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioWhen events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1;If risk was the same in both groups, the odds would be equal A comparison of odds, the odds ratio, might then make sense OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk


What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute
Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a study if there are no events in the control group This is because, as can be seen from the formulae in Box 92a, we would be trying to divide by zero The odds ratio also cannot be calculated if everybody in the intervention group experiences an event In these situations, and others where standard errors cannot be computedAnd a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19StATS Odds ratio versus relative risk (created by ) Dear Professor Mean There is some confusion about the use of the odds ratio versus the relative risk Can you explain the difference between these two numbers?


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
OR = odds ratio;In fact, the odds ratio has much more common use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk Because the (natural log of the) odds of a record is estimated as a linear function of the explanatory variables, the estimated odds ratio for 70yearolds and 60yearolds associated with the type of · Before we look at odds and risk ratios, let's be clear on what odds and probabilities are (this couple of paragraphs added on August 18) Using binomial versus quasibinomial does make a difference to confidence intervals, but in our current case it's not material The confidence intervals at least contain the correct values;



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
This implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Although the point estimate is biased



Nccmt Ure Relative Risk It S Easy To Calculate And Interpret Youtube



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram
The absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group · Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated However, it should be noted that, although, mathematical · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to
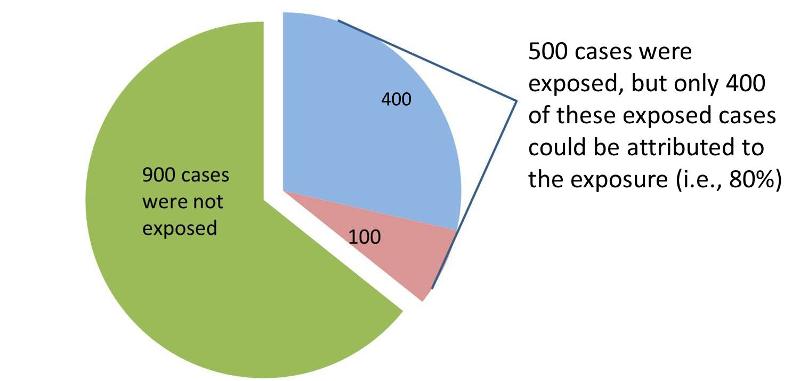


Measures Of Association


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk
· It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinity It is usually expressed as a ratio of two integers For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1 Back to the Superbowl example, the relative odds of being hungover today, associated with being a Seahawks fan · The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group However, this would



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
R C = absolute risk in the unexposed group, given as a fraction (for example fill in 10% risk as 01) Confusion and exaggeration Odds ratios have often been confused with relative risk in medical literature For nonstatisticians, the odds ratio is a difficult concept to comprehend, and it gives a more impressive figure for · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold; · So odds ratio are best used if followup time is fixed, for example if the outcome is measured at a specific followup visit or you have a casecontrol study Odds ratio = (odds in intervention group) / (odds in control group) Another slightly clunky interpretation here too!



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the likelihood of an event between two groups Consider the following data on survival of passengers · The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be used to approximate the relative risk of the event of



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Simple Rules On When And How To Use Them Mckenzie European Journal Of Clinical Investigation Wiley Online Library
Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert Genau so kommen Experten auf populäre Zeilen wie "Gewöhnliche alkoholische Getränketrinker sind 24 mal mehr gefährdet, an Leberproblemen · That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculatedThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Relative risk assessment statistics are particularly suited to



Odds Ratio For Myocardial Infarction Risk Factors Worldwide Old 53 Download Scientific Diagram


Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
A nonmemorization method of dealing with RR and OR*USMLE is a registered trademark of its respective holder I am in no way affiliated with itDisclaimer · Risk Ratio = / = 058 Note that the "exposure" of interest was lowdose aspirin, and the aspirin group is summarized in the top row The group assigned to take aspirin had an incidence of 126%, while the placebo (unexposed) group had an incidence of about 217% The cumulative incidence in the aspirin group was divided by the cumulative incidence in the placebo · Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group
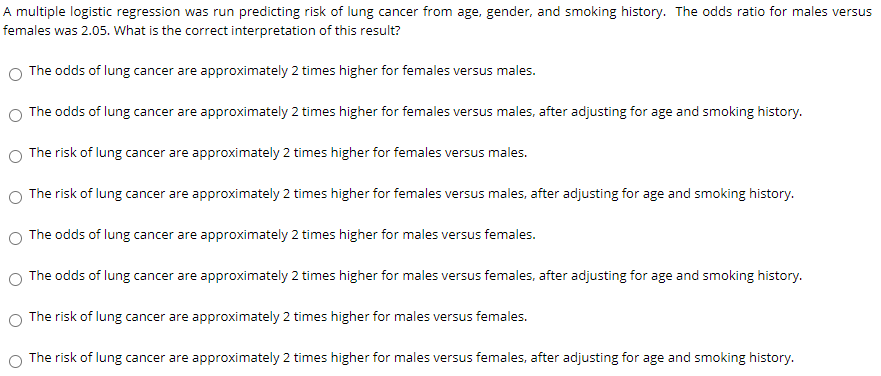


Solved A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com



Odds Ratio Relative Risk
· Risk Ratios Versus Odds Ratios When a study has a binary outcome (eg, disease or no disease), then investigators can calculate risk ratios and odds ratios Risk and odds ratios are calculated by using either cumulative risk (from longitudinal studies) or prevalence (from cross‐sectional studies) The risk ratio gives the relative increase or decrease in the risk (orOdds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used to approximate the relative risk of the event ofOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, and in cohort studies in which the
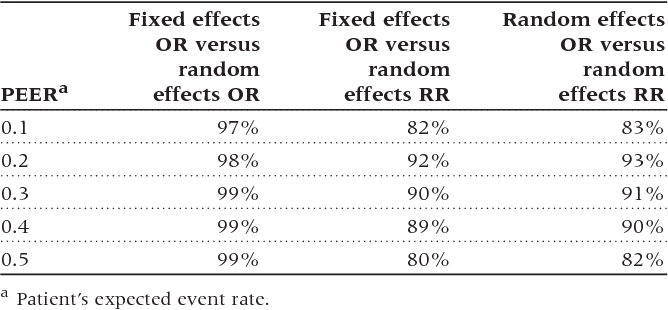


Table 2 From Can We Individualize The Number Needed To Treat An Empirical Study Of Summary Effect Measures In Meta Analyses Semantic Scholar



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
· Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents"increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are at 069 times the risk/chance of women" Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 noOdds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Lorsque deux groupes sont en cours d'étude ou d'observation, vous pouvez utiliser deux mesures pour décrire la probabilité comparative d'un événement Ces deux mesures sont l'odds ratio et le risque relatif Les deux sont deux concepts statistiques différents, bien que tellement liés les uns aux autres



Odds Ratio Article


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
This video demonstrates how to calculate odds ratio and relative risk values using the statistical software program SPSSSPSS can be used to determine odds rThe odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretation that most people make There are some · A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group Percent Relative Effect An alternative way to look at and interpret these comparisons would be to compute the percent relative effect (the percent change in the exposed group) In essence, we regard the unexposed group as having 100% of the risk and express the exposed group relative to that For example,



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR will



Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club
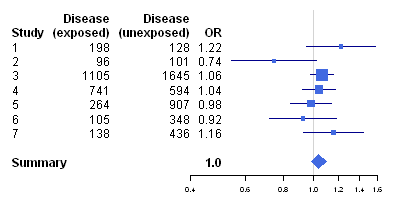


Using R For Biomedical Statistics Biomedical Statistics 0 2 Documentation



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table



Risk Differences And Rate Differences
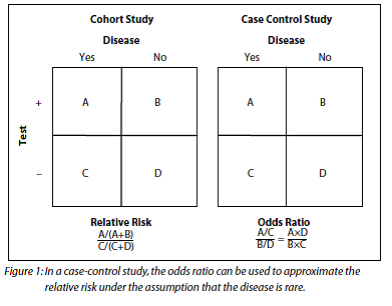


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence


Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia


The Difference Between Probability And Odds



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Ranganathan P Aggarwal R Pramesh C S Perspect Clin Res



Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
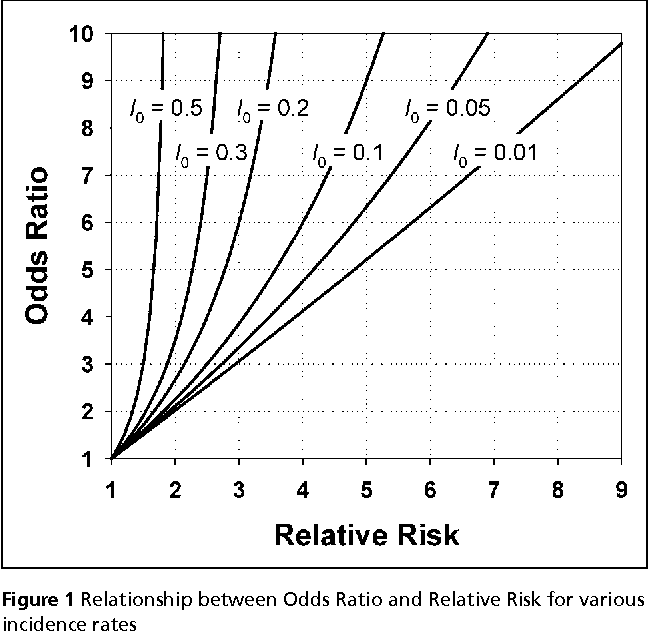


Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
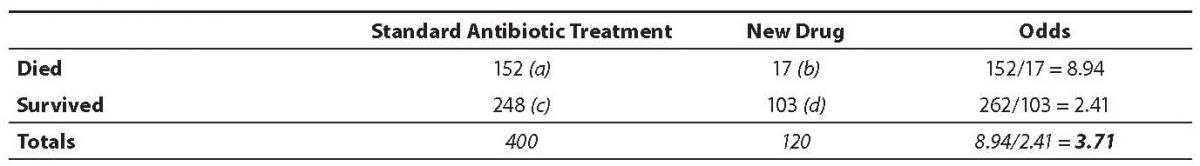


The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube


Proportions Chi Squared Tests And Odds Ratios



Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table



Power Calculations For Gwass The Smallest Odds Ratio Case Control Download Scientific Diagram



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect
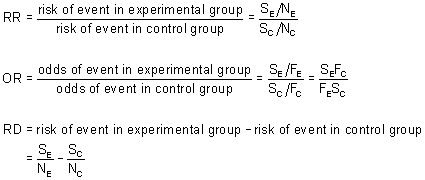


Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



The Diagnostic Odds Ratio A Single Indicator Of Test Performance Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download



Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study



Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Od Chegg Com


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk


How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A Few Colorful Figures Our Data Generation


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect


Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



Solved 4 In A Cohort Study The Risk Ratio For Copd For M Chegg Com
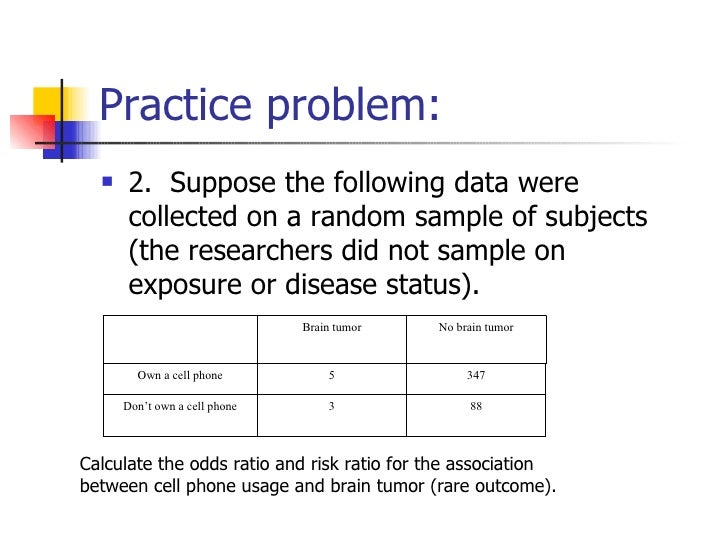


Lecture3



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training


Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge



Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Pooled Odds Ratio Or Of Risk Of Mortality In Vitamin D Deficient Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
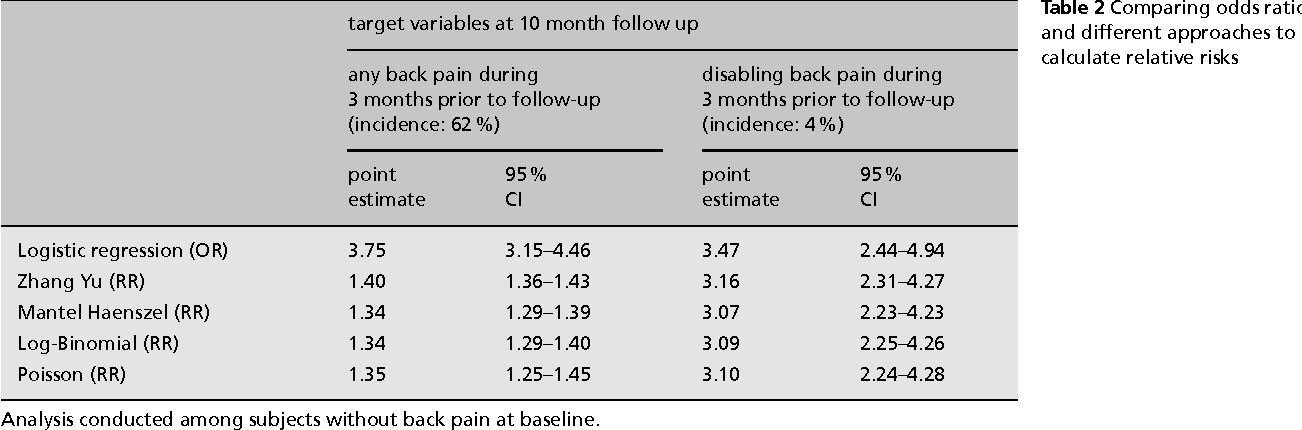


Figure 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
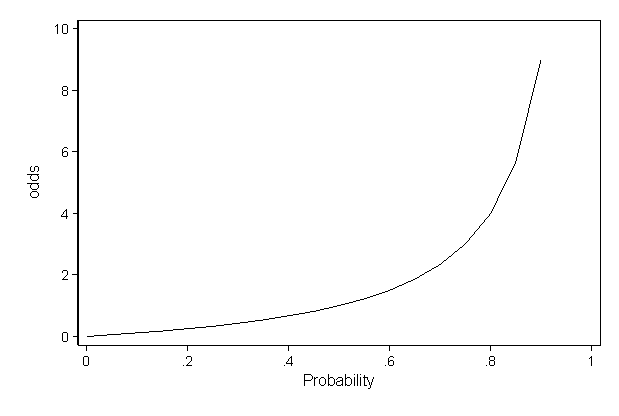


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk


Stats Guidelines For Logistic Regression Models September 27 1999



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿